SD-Fabric Deployment (Beta)
Note
SD-Fabric using the P4 UPF is a beta feature in the Aether 1.5 release, and the hardware and software setup is not required if using the BESS UPF.
Update aether-pod-configs
aether-pod-configs is a git project hosted on gerrit.opencord.org and
we placed the following materials in it.
Terraform scripts to install SD-Fabric applications on Rancher, including ONOS, Stratum and Telegraf.
Customized configuration for each application (helm values).
Application specific configuration files, including ONOS network configuration and Stratum chassis config.
Here is an example folder structure:
╰─$ tree staging/stg-ace-menlo/sdfabric
staging/stg-ace-menlo/sdfabric
├── app_map.tfvars
├── backend.tf
├── main.tf -> ../../../common/sdfabric/main.tf
├── sdfabric
│ ├── app_map.tfvars
│ ├── backend.tf
│ ├── kubeconfig -> ../../../../common/sdfabric/apps/onos/kubeconfig
│ ├── leaf1-chassis-config.pb.txt
│ ├── leaf2-chassis-config.pb.txt
│ ├── main.tf -> ../../../../common/sdfabric/apps/sdfabric/main.tf
│ ├── sdfabric.yaml
│ ├── spine1-chassis-config.pb.txt
│ ├── spine2-chassis-config.pb.txt
│ └── variables.tf -> ../../../../common/sdfabric/apps/sdfabric/variables.tf
├── telegraf
│ ├── app_map.tfvars
│ ├── backend.tf
│ ├── main.tf -> ../../../../common/sdfabric/apps/telegraf/main.tf
│ ├── telegraf.yaml
│ └── variables.tf -> ../../../../common/sdfabric/apps/telegraf/variables.tf
└── variables.tf -> ../../../common/tost/variables.tf
There are three Terraform scripts inside sdfabric directory and are responsible for managing each service.
Root folder
Terraform reads app_map.tfvars to know which application will be installed on Rancher and which version and customized values need to apply to.
Here is the example of app_map.tfvars which defines prerequisite apps for SD-Fabric as well as project and namespace in which SD-fabric apps will be provisioned. Note that currently we don’t have any prerequisite so we left this blank intentionally. It can be used to specify prerequisites in the future.
project_name = "sdfabric"
namespace_name = "tost"
SD-FABRIC folder
All files under onos directory are related to ONOS application. The app_map.tfvars in this folder describes the information about ONOS helm chart.
In this example, we specify the onos-tost helm chart version to 0.1.18 and load onos.yaml as custom value files.
apps = ["onos"]
namespace_name = "tost"
app_map = {
sdfabric = {
app_name = "onos-tost"
repo_name = "aether"
chart_name = "sdfabric"
chart_version = "1.0.7"
values_yaml = "sdfabric.yaml"
}
}
sdfabric.yaml used to custom your sdfabric Helm chart values and please check SD-Fabric Helm chart to see how to configure it.
Once the Stratum is deployed to Kubernetes, it will read switch-dependent config files from the aether-pod-configs repo. The key folder(stratum.config.folder) indicates that relative path of configs.
Attention
The switch-dependent config file should be named as ${hostname}-chassis-config.pb.txt. For example, if the host name of your Tofino switch is my-leaf, please name config file my-leaf-config.pb.txt.
Telegraf folder
The app_map.tfvars specify the Helm Chart version and the filename of the custom Helm value file.
apps=["telegraf"]
namespace_name = "tost"
app_map = {
telegraf = {
app_name = "telegraf"
repo_name = "aether"
chart_name = "tost-telegraf"
chart_version = "0.1.5"
values_yaml = "telegraf.yaml"
}
}
The telegraf.yaml used to override the ONOS-Telegraf Helm Chart and its environment-dependent. Please pay attention to the inputs.addresses section. Telegraf will read data from stratum so we need to specify all Tofino switch’s IP addresses here. Taking Menlo staging pod as example, there are four switches so we fill out 4 IP addresses.
podAnnotations:
field.cattle.io/workloadMetrics: '[{"path":"/metrics","port":9273,"schema":"HTTP"}]'
config:
outputs:
- prometheus_client:
metric_version: 2
listen: ":9273"
inputs:
- cisco_telemetry_gnmi:
addresses:
- 10.92.1.81:9339
- 10.92.1.82:9339
- 10.92.1.83:9339
- 10.92.1.84:9339
redial: 10s
- cisco_telemetry_gnmi.subscription:
name: stratum_counters
origin: openconfig-interfaces
path: /interfaces/interface[name=*]/state/counters
sample_interval: 5000ns
subscription_mode: sample
Create Your Own Configs
The easiest way to create your own configs is running the template script.
Assumed we would like to set up the ace-example pod in the production environment.
open the tools/ace_config.yaml (You should already have this file when you finish VPN bootstrap stage)
fill out all required variables
perform the makefile command to generate configuration and directory for SD-Fabric
update onos.yaml for ONOS
update ${hostname}-chassis-config.pb.txt for Stratum
commit your change and open the Gerrit patch
deploy your patch to ACE cluster and merge it after verifying the fabric connectivity
vim tools/ace_config.yaml
make -C tools sdfabric
vim production/ace-example/sdfabric/sdfabric/sdfabric.yaml
vim production/ace-example/sdfabric/sdfabric/*${hostname}-chassis-config.pb.txt**
git add commit
git review
Quick recap
To recap, most of the files in tost folder can be copied from existing examples. However, there are a few files we need to pay extra attentions to.
sdfabric.yaml in sdfabric folder
Chassis config in sdfabric folder There should be one chassis config for each switch. The file name needs to be ${hostname}-chassis-config.pb.txt
telegraf.yaml in telegraf folder need to be updated with all switch IP addresses
Double check these files and make sure they have been updated accordingly.
Create a review request
We also need to create a gerrit review request, similar to what we have done in the Aether Runtime Deployment.
Please refer to Aether Runtime Deployment to create a review request.
Deploy to ACE cluster
SD-Fabric is environment dependent application and you have to prepare correct configurations for both ONOS and Stratum to make it work.
A recommended approach is verifying your patch before merging it. You can type the comment apply-all in the Gerrit patch to trigger the deployment process, and then start to verify fabric connectivity.
Attention
Due to the limitation of Terraform’s dependent issue, you have to type the comment apply-all to trigger root folder’s Terraform script to setup project and namespace before merging the patch.
Check below section to learn more about how we setup the Jenkins job and how it works
Create SD-Fabric (named TOST in Jenkins) deployment job in Jenkins
There are three major components in the Jenkins system, the Jenkins pipeline and Jenkins Job Builder and Jenkins Job.
We follow the Infrastructure as Code principle to place three major components
in a Git repo, aether-ci-management
Download the aether-ci-management repository.
$ cd $WORKDIR
$ git clone "ssh://[username]@gerrit.opencord.org:29418/aether-ci-management"
Here is the example of folder structure, we put everything related to three major components under the jjb folder.
$ tree -d jjb
jjb
├── ci-management
├── global
│ ├── jenkins-admin -> ../../global-jjb/jenkins-admin
│ ├── jenkins-init-scripts -> ../../global-jjb/jenkins-init-scripts
│ ├── jjb -> ../../global-jjb/jjb
│ └── shell -> ../../global-jjb/shell
├── pipeline
├── repos
├── shell
└── templates
Jenkins pipeline
Jenkins pipeline runs the Terraform scripts to install desired applications into the specified Kubernetes cluster.
Both ONOS and Stratum will read configuration files (network config, chassis config) from aether-pod-config.
The default git branch is master. For testing purpose, we also provide two parameters to specify the number of reviews and patchset.
We will explain more in the next section.
Note
Currently, we don’t perform the incremental upgrade for SD-Fabric application. Instead, we perform the clean installation. In the pipeline script, Terraform will destroy all existing resources and then create them again.
We put all pipeline scripts under the pipeline directory, the language of the pipeline script is groovy.
$ tree pipeline
pipeline
├── aether-in-a-box.groovy
├── artifact-release.groovy
├── cd-pipeline-charts-postrelease.groovy
├── cd-pipeline-dockerhub-postrelease.groovy
├── cd-pipeline-postrelease.groovy
├── cd-pipeline-terraform.groovy
├── docker-publish.groovy
├── ng40-func.groovy
├── ng40-scale.groovy
├── reuse-scan-gerrit.groovy
├── reuse-scan-github.groovy
├── tost-onos.groovy
├── tost-stratum.groovy
├── tost-telegraf.groovy
└── tost.groovy
Currently, we had five pipeline scripts for SD-Fabric deployment.
tost.groovy
sdfabric.groovy
tost-telegraf.groovy
tost-onos-debug.groovy
sdfabric.groovy and tost-telegraf.groovy are used to deploy the individual application respectively, and tost.groovy is a high level script, used to deploy whole SD-Fabric application, it will execute the above three scripts in its pipeline script.
tost-onos-debug.groovy is used to dump the debug information from the ONOS controller and it will be executed automatically when ONOS is deployed.
Jenkins jobs
Jenkins job is the task unit in the Jenkins system. A Jenkins job contains the following information:
Jenkins pipeline
Parameters for Jenkins pipeline
Build trigger
Source code management
We created one Jenkins job for each SD-Fabric component, per Aether edge.
We have four Jenkins jobs (HostPath provisioner, ONOS, Stratum and Telegraf) for each edge as of today.
There are 10+ parameters in Jenkins jobs and they can be divided into two parts, cluster-level and application-level.
Here is an example of supported parameters.
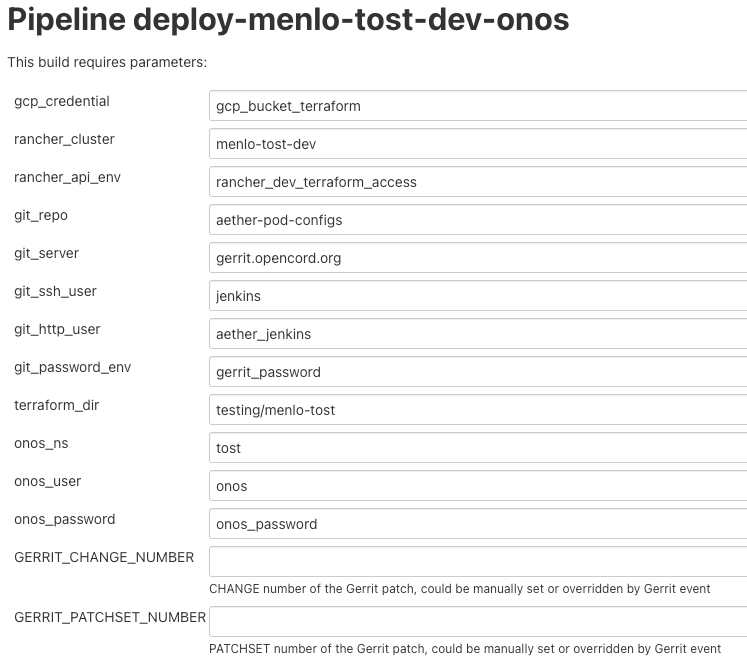
Application level
GERRIT_CHANGE_NUMBER/GERRIT_PATCHSET_NUMBER: tell the pipeline script to read the config for aether-pod-configs repo from a specified gerrit review, instead of the HEAD branch. It’s good for developer to test its change before merge.
onos_user: used to login ONOS controller
git_repo/git_server/git_user/git_password_env: information of git repository, git_password_env is a key for Jenkins Credential system.
Cluster level
gcp_credential: Google Cloud Platform credential for remote storage, used by Terraform.
terraform_dir: The root directory of the SD-Fabric directory.
rancher_cluster: target Rancher cluster name.
rancher_api_env: Rancher credential to access Rancher, used by Terraform.
Note
Typically, developer only focus on GERRIT_CHANGE_NUMBER and GERRIT_PATCHSET_NUMBER. The rest of them are managed by OPs.
Jenkins Job Builder (JJB)
We prefer to apply the IaC (Infrastructure as Code) for everything. We use the JJB (Jenkins Job Builder) to create new Jenkins Job, including the Jenkins pipeline. We need to clone a set of Jenkins jobs when a new edge is deployed.
In order to provide the flexibility and avoid re-inventing the wheel, we used the job template to declare your job. Thanks to the JJB, we can use the parameters in the job template to render different kinds of jobs easily.
All the template files are placed under templates directory.
╰─$ tree templates
templates
├── aether-in-a-box.yaml
├── archive-artifacts.yaml
├── artifact-release.yml
├── cd-pipeline-terraform.yaml
├── docker-publish-github.yaml
├── docker-publish.yaml
├── helm-lint.yaml
├── make-test.yaml
├── ng40-nightly.yaml
├── ng40-test.yaml
├── private-docker-publish.yaml
├── private-make-test.yaml
├── publish-helm-repo.yaml
├── reuse-gerrit.yaml
├── reuse-github.yaml
├── sync-dir.yaml
├── tost.yaml
├── verify-licensed.yaml
└── versioning.yaml
We defined all SD-Fabric required job templates in tost.yaml and here is its partial content.
- job-template:
name: "{name}-onos"
id: "deploy-onos"
project-type: pipeline
dsl: !include-raw-escape: jjb/pipeline/tost-onos.groovy
triggers:
- onf-infra-tost-gerrit-trigger:
gerrit-server-name: '{gerrit-server-name}'
trigger_command: "apply"
pattern: "{terraform_dir}/tost/onos/.*"
logrotate:
daysToKeep: 7
numToKeep: 10
artifactDaysToKeep: 7
artifactNumToKeep: 10
parameters:
- string:
name: gcp_credential
default: "{google_bucket_access}"
- string:
name: rancher_cluster
default: "{rancher_cluster}"
- string:
name: rancher_api_env
default: "{rancher_api}"
- string:
name: git_repo
default: "aether-pod-configs"
- string:
name: git_server
default: "gerrit.opencord.org"
- string:
name: git_ssh_user
default: "jenkins"
Once we have the job template, we need to tell the JJB, we want to use the job template to create our own jobs. Here comes the concept of project, you need to define job templates you want to use and the values of all parameters.
We put all project yaml files under the repo directory and here is the example
╰─$ tree repos 130 ↵
repos
├── aether-helm-charts.yaml
├── aether-in-a-box.yaml
├── cd-pipeline-terraform.yaml
├── ng40-test.yaml
├── spgw.yaml
└── tost.yaml
Following is the example of tost projects, we defined three projects here, and each project has different parameters and Jenkins jobs it wants to use.
- project:
name: deploy-tucson-pairedleaves-dev
rancher_cluster: "dev-pairedleaves-tucson"
terraform_dir: "staging/dev-pairedleaves-tucson"
rancher_api: "{rancher_staging_access}"
properties:
- onf-infra-onfstaff-private
jobs:
- "deploy"
- "deploy-onos"
- "deploy-stratum"
- "deploy-telegraf"
- "debug-tost"
Create Your Own Jenkins Job
Basically, if you don’t need to customize the Jenkins pipeline script and the job configuration, the only thing you need to do is modify the repos/tost.yaml to add your project.
For example, we would like to deploy the SD-Fabric to our production pod, let’s assume it named “tost-example”. Add the following content into repos/tost.yaml
- project:
name: deploy-tost-example-production
rancher_cluster: "ace-test-example"
terraform_dir: "production/tost-example"
rancher_api: "{rancher_production_access}"
disable-job: false
need_stratum: false
need_onos: false
need_sdfabric: true
debug_namespace: tost
topology:
- sdfabric
properties:
- onf-infra-onfstaff-private
jobs:
- "deploy"
trigger_path: "sdfabric/.*
- "deploy-sdfabric"
- "deploy-telegraf"
- "debug-tost"
Note
The terraform_dir indicates the directory location in aether-pod-configs repo, please ensure your Terraform scripts already there before running the Jenkins job.
Trigger SD-Fabric (named TOST in Jenkins) deployment in Jenkins
Whenever a change is merged into aether-pod-config, the Jenkins job should be triggered automatically to (re)deploy SD-Fabric (named TOST in Jenkins).
You can also type the comment apply in the Gerrit patch, it will trigger Jenkins jobs to deploy SD-Fabric for you.
Verification
Fabric connectivity should be fully ready at this point. We should verify that all servers, including compute nodes and the management server, have an IP address and are able to reach each other via fabric interface before continuing the next step.
This can be simply done by running a ping command from one server to another server’s fabric IP.
Disable deployment jobs
After verifying the SD-Fabric is ready, please submit another patch to disable the job.
$ cd $WORKDIR/aether-ci-management
$ vi jjb/repos/tost.yaml
# Add jobs for the new cluster
diff --git a/jjb/repos/tost.yaml b/jjb/repos/tost.yaml
index 19bade4..81b4ab1 100644
--- a/jjb/repos/tost.yaml
+++ b/jjb/repos/tost.yaml
@@ -478,7 +478,7 @@
rancher_cluster: "ace-ntt"
terraform_dir: "production/ace-ntt"
rancher_api: "{rancher_production_access}"
- disable-job: false
+ disable-job: true
properties:
- onf-infra-onfstaff-private
jobs:
Troubleshooting
The deployment process involves the following steps:
Jenkins Job
Jenkins Pipeline
Clone Git Repository
Execute Terraform scripts
Rancher start to install applications
Applications be deployed into Kubernetes cluster
ONOS/Stratum will read the configuration (network config, chassis config)
Pod become running
Taking ONOS as an example, here’s what you can do to troubleshoot.
You can see the log message of the first 4 steps in Jenkins console. If something goes wrong, the status of the Jenkins job will be in red. If Jenkins doesn’t report any error message, the next step is going to Rancher’s portal to ensure the Answers is same as the onos.yaml in aether-pod-configs.
Accessing the Stratum CLI
You can login to the Stratum container running on a switch using this script:
#!/bin/bash
echo 'Attaching to Stratum container. Ctrl-P Ctrl-Q to exit'
echo 'Press Enter to continue...'
DOCKER_ID=`docker ps | grep stratum-bf | awk '{print $1}'`
docker attach $DOCKER_ID
You should then see the bf_sde prompt:
bf_sde> pm
bf_sde.pm> show -a
Accessing the ONOS CLI
After setting up kubectl to access the SD-Fabric pods, run:
$ kubectl get pods -n tost
Pick a SD-Fabric pod, and make a port forward to it, then login to it with the
onos CLI tool:
$ kubectl -n tost port-forward onos-tost-onos-classic-0 8181 8101
$ onos karaf@localhost
In some rare cases, you may need to access the ONOS master instance CLI, in
which case you can run roles:
karaf@root > roles
device:devswitch1: master=onos-tost-onos-classic-1, standbys=[ onos-tost-onos-classic-0 ]
Above lines show that onos-tost-onos-classic-1 is the master. So switch to
that by killing the port forward, starting a new one pointing at the master,
then logging into that one:
$ ps ax | grep -i kubectl
# returns kubectl commands running, pick the port-forward one and kill it
$ kill 0123
$ kubectl -n tost port-forward onos-tost-onos-classic-1 8181 8101
$ onos karaf@localhost